Summary
A novel machine learning algorithm that addresses the problem of stratification of patients at risk of coronary plaque progression using IVUS images and standard patient clinical data.
Inventors
Hector Garcia-Garcia, MD, PhD
Pablo J. Blanco
Carlos A. Bulant
What is it? What does it do?
Due to the major mortality and morbidity burden of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) caused by plaque rupture and erosion, coronary plaque progression and inflammation are major targets for pharmacotherapy. The ability to predict plaque burden progression and whether or not patients would respond favorably to treatments would significantly improve patient risk stratification and support tailored interventions.
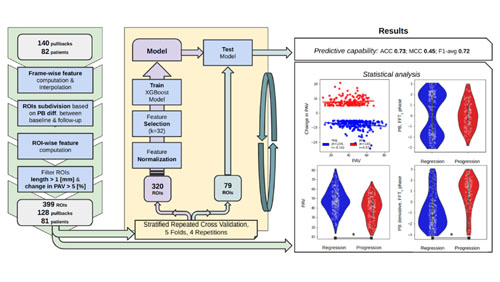
The novel machine learning algorithm is able to predict atherosclerotic plaque progression and regression changes in coronary IVUS images and standard clinical data from patients treated with rosuvastatin therapy in 13 months. Change in the percent of atheroma volume (∆PAV) is used as the endpoint and predictions are determined at a region-wise level, instead of frame-level, resulting in better accuracy.
Why is it better?
This first-of-its-kind machine learning model:
-
Uses SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values to enhance interpretability of the predicted outcome.
-
Eliminates heavy image processing, simulations, and additional computational models.
-
Leverages a novel methodology using regions instead of frames to provide a more robust and accurate prediction of changes in plaque burden over time.
What is its current status?
This machine learning algorithm was developed using a subset of data from the IBIS-4 clinical trial which included 140 IVUS pullbacks from 81 patients. An XGBoost regressor was used for the model estimates of ∆PAV, which were determined with five-fold cross validation (at the patient level) and 20 repetitions to assess model performance.
MedStar Inventor Services filed a provisional patent (63/591,518) prior to submission of journal publication.
The MedStar Inventor Services team is now seeking a licensing/collaboration partner to help advance and commercialize this technology. Please contact us at invent@medstar.net.