Summary
A novel angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance (IMRangio) provides an accurate and non-invasive option for the assessment of coronary microcirculation in a spectrum of coronary syndromes.
Inventors
Hector Garcia-Garcia, MD, PhD
Giovanni Luigi De Maria, MD, PhD
Adrian Banning, MD
What is it? What does it do?
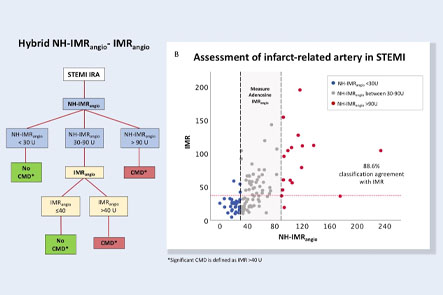
Coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD) is a condition in which a patient has abnormalities in the small blood vessels of the heart. Despite its well-reported clinical and prognostic implications, CMD is often underdiagnosed in patients with coronary artery disease. Currently, the standard for diagnosis is the index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR). Unfortunately, identifying, minimizing, and potentially reversing microvascular injury is made difficult due to the procedural time, costs, and technical complexities related to detection, such as the related pressure-wire manipulation and the need for adenosine infusion for maximal hyperaemia related to use of the IMR.
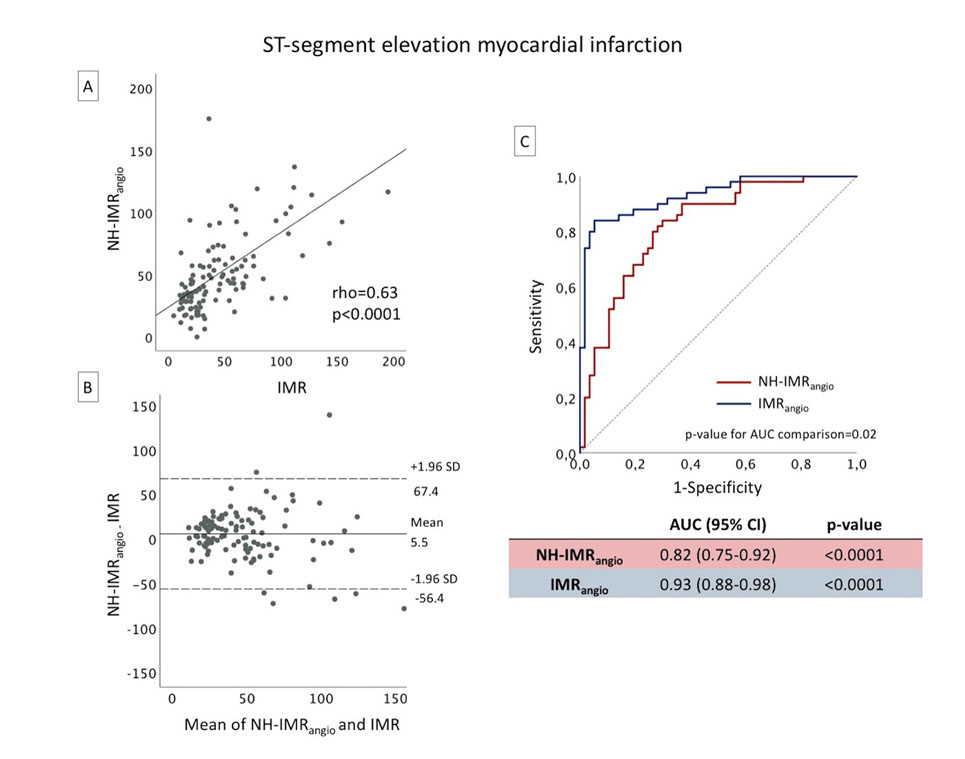
The novel angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance (IMRangio) was developed from unique machine learning algorithms that are used to perform computational flow analysis from a series of medical images. The index provides a safer way to produce diagnostic data that significantly correlates with the IMR.
Why is it better?
-
IMRangio is a safer method for CMD diagnosis as it removes the need for the invasive pressure-wire procedure and unnecessary introduction of adenosine.
-
The index is more cost-effective through a decrease in the clinical time needed for CMD diagnostics.
-
IMRangio has the potential for broader application and may be used to assess the entire spectrum of coronary syndromes such as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS), and chronic coronary syndrome (CCS).
What is its current status?
The IMRangio was developed and validated using quantitative flow ratio (QFR) at rest and hyperaemia in STEMI, NSTEMI, and CCS patients. This is an extension of previous work developed for STEMI-only patients.
MedStar Inventor Services performed a patentability and market analysis assessment on the invention, including a detailed report on the clinical need and competitive landscape. A PCT was filed based on their findings. Presently, U.S. and European patent applications are undergoing patent prosecution.
|
Patent |
Status |
| US17/068,368 | Pending |
| EP20875626.2A | Pending |
| PCT/US2020/055240 | Filed |
The MedStar Inventor Services team is now seeking a licensing/collaboration partner to help advance and commercialize this technology. Please contact us at invent@medstar.net.
Publications
-
Scarsini, R., Shanmuganathan, M., Kotronias, R. A., Terentes-Printzios, D., Borlotti, A., Langrish, J. P., ... & De Maria, G. L. (2021). Angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance (IMRangio) as a novel pressure-wire-free tool to assess coronary microvascular dysfunction in acute coronary syndromes and stable coronary artery disease. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 37(6), 1801-1813.
-
De Maria, G. L., Scarsini, R., Shanmuganathan, M., Kotronias, R. A., Terentes-Printzios, D., Borlotti, A., ... & Banning, A. P. (2020). Angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance as a novel, pressure-wire-free tool to assess coronary microcirculation in ST elevation myocardial infarction. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 36, 1395-1406.
-
Fernández‐Peregrina, E., Garcia‐Garcia, H. M., Sans‐Rosello, J., Sanz‐Sanchez, J., Kotronias, R., Scarsini, R., ... & De Maria, G. L. (2022). Angiography‐derived versus invasively‐determined index of microcirculatory resistance in the assessment of coronary microcirculation: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 99(7), 2018-2025.
-
Kotronias, R. A., Terentes-Printzios, D., Shanmuganathan, M., Marin, F., Scarsini, R., Bradley-Watson, J., ... & De Maria, G. L. (2021). Long-term clinical outcomes in patients with an acute ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction stratified by angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 8, 717114.
-
Sans-Roselló, J., Fernández-Peregrina, E., Duran-Cambra, A., Carreras-Mora, J., Sionis, A., Álvarez-García, J., & Garcia-Garcia, H. M. (2021). Coronary microvascular dysfunction in takotsubo syndrome assessed by angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance: a pressure-wire-free tool. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4331.